简介
本文对于所有在 MQL 环境下编程的人员,无论是初学者还是专业人士,将会非常有趣。而且 MQL 环境下的开发人员和理论家阅读此文也会相当有帮助,因为这里所分析的问题可能会成为将来实施 MetaTrader 和 MQL 的项目。在某些程度上,类似的想法可见于文章通用的 Expert Advisor 模板和在通用的 Expert Advisor 中发送交易信号
所以,
依我作为一个程序员看来,MQL 的劣势之一是在构建交易系统模型时缺少对象方法。MQL 开发者给我们提供了两种解决方法:调用外部函数或使用有序参数 MAGIC 来识别序号归属。
实际上,如果只有一个系统在一个帐户运行,我们不需要识别。但当我们具有在一个帐户上添加多个自动交易系统的程序选项时,就不得不使用 MAGIC 了。即使在调用外部函数时,也需要进行确定。当然,我们可以建立一个 OrderTicket 数组并识别仅属于一个交易系统的数组,但据我们对一些经纪公司的了解,委托单在交换时(即一个订单关闭,另一个订单打开)会改变。这就是我们必须使用 MAGIC 的原因。
所以,在开发者们忙于改善 MQL 语言,使其更加灵活时,我们在建立交易模型时采用对象方法。
这是一个跟我的对象模型一致的交易系统。当然,这并非通用,但目前我没有发现其他方法。
所以,我们来分析该模型。
A).信号系统(SS)
该模块过程的对象和理解即将出现的报价。通常,信号系统的“对象”是一组指标,例如,移动平均线指标。根据处理的报价和指标值,“对象”(或信号量)产生信号以进入/退出或改动订单等。
信号量形成其信号并从进入/退出(EE)模块发送至另一个对象。。
在 MQL 中设置信号量相当容易。
1.使用 #define 定义全局标识符。
最好不要设置连续的数字,例如 1、2、3、4...,而是在 5-10,这样在 Expert Advisor 内我们可以将一个信号用于多个进程(见第二个模块)。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Signals.mqh | //| Copyright © 2007 Сергеев Алексей | //| los@we.kherson.ua | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright © 2007, Сергеев Алексей " #property link "mailto: los@we.kherson.ua" #property library #define BLACKSYS 10 #define BORCHAN 20 #define ELDER 80 #define ENVELOP 90
2.然后在该模块的全局函数中我们应该启用其处理程序。
int CheckSignal(bool bEntry, int SignalID) { switch (SignalID) { case BLACKSYS: return (BlackSys(bEntry)); break; case BORCHAN: return (BorChan(bEntry)); break; case ELDER: return (Elder(bEntry)); break; case ENVELOP: return (Envelop(bEntry)); break; default: return (-1); } }
3.最后一步是对函数的描述。
下面是一个对象的处理信号的示例,该对象继承了包络线指标的特征。
int Envelope(bool bEntry) { int MA=21; double Deviation=0.6; int Mode=MODE_SMA;//0-sma, 1-ema, 2-smma, 3-lwma int Price=PRICE_CLOSE;//0-close, 1-open, 2-high, 3-low, 4-median, 5-typic, 6-wieight double envH0, envL0, m0; double envH1, envL1, m1; envH0=iEnvelopes(NULL, 0, MA, Mode, 0, Price, Deviation, MODE_UPPER, 0); envL0=iEnvelopes(NULL, 0, MA, Mode, 0, Price, Deviation, MODE_LOWER, 0); envH1=iEnvelopes(NULL, 0, MA, Mode, 0, Price, Deviation, MODE_UPPER, 1); envL1=iEnvelopes(NULL, 0, MA, Mode, 0, Price, Deviation, MODE_LOWER, 1); m0 = (Low[0]+High[0])/2; m1 = (Low[1]+High[1])/2; //----- condition for operation execution if (bEntry) //for opening { if (envH0<m0 && envH1<m1) return (OP_SELL); if (envL0>m0 && envL1>m1) return (OP_BUY); } else //for closing { if (envH0<m0 && envH1<m1) return (OP_BUY); if (envL0>m0 && envL1>m1) return (OP_SELL); } return (-1); //no signal }
这样我们就得到一个包含不同对象信号的模块。
B).EE 程序块的对象具有最小的任务:首先,其对象跟对象信号交互作用——注意观察。生命周期和互动如下:Checking semaphore -> if there are any positive signals, open/close/modify positions -> Passing control to objects in the module PS.EE 模块中的所有对象都有一个前缀进程...,更加具体的确定了其行为。
例如:
ProcessAvgLim // - the object processes signals with opening pending limit-orders and positions averaging ProcessTurn // - the object processes signals with position turning
交易系统类别的每一个样本(我们对此都理解并在模块中使用)必须具有其自己独立的特征,比如获利、止损、自己的资金管理以及在不同的跟踪变体中使用的其他补充参数等。
在使用这些特征时,我尝试了多种方法,发现在 MQL 中最适合的是创建一个二维数组。以下是它的描述:
double SysPar[nSignal][11]; #define _TP 0 // Profit #define _NullTP 1 // profit level, after which we set into losslessness #define _NullTP2 2 // profit level, after which we set into losslessness #define _TS 3 // distance of the trailing stop #define _NullSL 4 // level, after achieving which the expected profit is transfered into opening point #define _SL 5 // level, after achieving which the expected profit is transfered into opening point #define _dSL 6 // the initial step upon the opening level of the next order in the position support #define _dStep 7 // The step is increased in .. times upon the level of the next opening #define _dLot 8 // In how many times (as compared to the last one) we increase the lot on the next one #define _nLot 9 // In how many times (as compared to the initial one) we increase the lot on the next one string SysParName[nSignal];
其中:nSignal 是对象信号的标识符。
例如:
SysPar[ENVELOP][_TS] = 40.0; // distance of the trailing stop SysPar[ENVELOP][_NullSL] = 20.0;// level, after achieving which the expected profit is transfered into opening point SysPar[ENVELOP][_SL] = 70; // changing stop-loss
根据你自己的要求,可以增加该数组结构中设定参数的数量。
在设置参数后,我们调用信号量处理的函数。换言之,我们跟信号系统交互。这通过我最喜欢的 start() 函数完成。
void start()
{
ProcessAvgLim(ENVELOP, ENVELOP, Green, Red);
… …
从规划可以看出,在交易系统中我们有 4 个注册信号量和 3 个观察器。每个信号量都基于自己的报价解读变体。
例如,信号量 1发送分析 MACD 指标的信号。。观察器 1 在接收到这些信号后在一个简单规划 ProcessSimple 中打开订单。ProcessSimple。
观察器 2 和 3 更加困难。每一个都控制两个信号量的信号。因此,订单打开的方法不同。
在设置了观察器的参数并添加信号量之后,我们需要控制和跟踪打开头寸。
“负责”已打开的订单状态的是 头寸支持(PS)模块的对象。
C).PS 程序块在我看来是最有趣的一个,重要性不亚于信号量。
在这里使用了不同的跟踪变体,挂单打开,头寸支持和锁定、获利和亏损控制的实施等。这种 PS 应对 EE 信号反应充分,在出现亏损头寸时退出市场将亏损降到最低。
下面这个网站有一个有趣的跟踪变体库:Library of Functions and Expert Advisors for trailing / Yury Dzyuban。所有的跟踪类型都可以轻松添加到系统。
简单来说,所有的支持对象都从前缀跟踪变体开始...
方案如下:
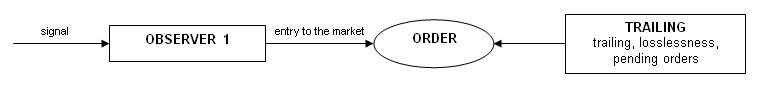
调用,控制从观察器到跟踪变体的传递也通过函数 start() 完成
void start()
{
ProcessSimple(MACD, MACD, Black, Plum); TrailingSimple(MACD, Black, Plum);
ProcessAvgLim(ENVELOPE, ENVELOPE, Green, Red); TrailingAvgLim(ENVELOPE, Green, Red);
}这是一个使用对象方法建立系统的示例变体。想要如此做的人可以使用。
我想再一次呼吁 MQL 开发者扩展语言选择。作为示例,以下是以 C++ 语言编写的执行对象类的变体。
struct SystemParam { double TP; // profit double NullTP; // profit level, after which we set into losslessness double NullTP2; // profit level, after which we set into losslessness a set of one-direction orders double TS; // distance of the trailing stop double NullSL; // loss level, at which we transfer the expected profit into losslessness double SL; // stop-loss double dSL; // a step upon the opening level of the next order for the position support double dStep; // In how many times we increase the step upon the opening level of the next order double dLot; // In how many times we increase the lot on the next order } class MTS { public: string m_NameTS; // system name (for making comments for the order) int m_SignalID; // identifier of trading signals (for semaphore inquiry) long int Tickets[1000]; // array of order tickets, selected upon m_SignalID (MAGIC) SystemParam SysPar; // Trading system parameters color ClrBuy; // color for indicating BUY order color ClrSell; // color for indicating SELL order // Initialization void MyMTS (); // standard function that sets initial values of the system void MyMTS (int aSignalID, int nProcessMode, int nTrailingMode); // standard function // that sets initial values of the system // Implementation int CheckSignal(); //function of checking state of market signals // Processing int m_nProcessMode; // identifier of observation mode int m_nTrailingMode; // identifier of trailing mode void Process(); // EE function - processing CheckSignal() void Trailing(); // PS function - order trailing // Special functions bool CreatTicketArray(int dir); // creating an array of tickets, selected upon m_SignalID (MAGIC) // and desired type dir: buy, sell, buylim, buystop, sellim, sellstop bool ArrangeOrderBy(int iSort); // arranging array Tickets upon the parameter (date, profit, price...) }; … MTS MyTS; // our trading system … int init() { … MyTS.m_SignalID = SIGNAL_MACD; // our system is based on MACD signals MyTS.m_NameTS = "MACD"; MyTS.SysPar.TP = 500; MyTS.SysPar.NullTP = 20; MyTS.SysPar.TS = 50; MyTS.SysPar.SL = 1000; MyTS.SetProcess (MODE_AVGLIM); MyTS.SetTrailing (MODE_AVGLIM); … } void start() { … MyTS.Process (); MyTS.Trailing (); … } … void MTS::Process() { … int Signal = CheckSignal(true, m_SignalID); //calling the global function of signal processing if (Signal == -1) return; // if no signal, do nothing //----- for buying if(Signal == OP_BUY) { } if(Signal == OP_SELL) { } … } … // global processor of semaphores int CheckSignal(bool bEntry, int SignalID) { switch (SignalID) { case ELDER: return (Elder(bEntry)); break; case ENVELOP: return (Envelop(bEntry)); break; case LAGUER: return (Laguer(bEntry)); break; case MACD: return (Macd(bEntry)); break; … } } // calling a certain semaphore int Macd(bool bEntry) { double MACDOpen=3; double MACDClose=2; double MA=26; int MODE_MA = MODE_EMA; // method of the calculation of averages int PRICE_MA = PRICE_CLOSE; // method of the calculation of averages int PERIOD = PERIOD_H1; // the period to work with //parameters of averages double MacdCur, MacdPre, SignalCur; double SignalPre, MaCur, MaPre; //---- get the value MacdCur=iMACD(NULL,0,8,17,9,PRICE_MA,MODE_MAIN,0); MacdPre=iMACD(NULL,0,8,17,9,PRICE_MA,MODE_MAIN,1); SignalCur=iMACD(NULL,0,8,17,9,PRICE_MA,MODE_SIGNAL,0); SignalPre=iMACD(NULL,0,8,17,9,PRICE_MA,MODE_SIGNAL,1); MaCur=iMA(NULL,0,MA,0,MODE_MA,PRICE_MA,0); MaPre=iMA(NULL,0,MA,0,MODE_MA,PRICE_MA,1); //----- condition for the operation execution if (bEntry) //for buying bEntry==true { if(MacdCur<0 && MacdCur>SignalCur && MacdPre<SignalPre && MathAbs(MacdCur)>(MACDOpen*Point) && MaCur>MaPre) return (OP_BUY); if(MacdCur>0 && MacdCur<SignalCur && MacdPre>SignalPre && MacdCur>(MACDOpen*Point) && MaCur<MaPre) return (OP_SELL); } else //for closing bEntry==false { if(MacdCur>0 && MacdCur<SignalCur && MacdPre>SignalPre && MacdCur>(MACDClose*Point)) return (OP_BUY); if(MacdCur>0 && MacdCur<SignalCur && MacdPre>SignalPre && MacdCur>(MACDOpen*Point) && MaCur<MaPre) return (OP_BUY); if(MacdCur<0 && MacdCur>SignalCur && MacdPre<SignalPre && MathAbs(MacdCur)>(MACDClose*Point)) return (OP_SELL); if(MacdCur<0 && MacdCur>SignalCur && MacdPre<SignalPre && MathAbs(MacdCur)>(MACDOpen*Point) && MaCur>MaPre) return (OP_SELL); } return (-1); //no signal }
MQL 语言中的系统逻辑没有多大不同。所有的函数变为全局性。为了区分两个交易系统的订单,我们需要向处理订单的所有函数添加 SignalID(即 MAGIC)。


