之前的文章研究了 点数图, Kagi 以及 Renko 图表。持续发表了一系列关于 20 世纪图表的文章,这次我们要谈的是三线突破图表,或者准确地说,关于通过程序代码来实现它。有关这张图表来源的信息非常少。我猜想它始于日本。在美国学到它们是在 1994 年出版的 Steve Nison 的 "Beyond Candlesticks(超越蜡烛条)" 。
除了上面提到的图表,并未谈及三线突破图表的构建时间范围。它基于确定时间帧中最后形成的收盘价格, 它可以过滤相对以前行情的小幅价格波动。
在 Steve Nison 著作 "Beyond Candlesticks(超越蜡烛条)" 中描述了 11 种绘制这个图表的原理(p. 185). 我已经将它们合并成三条。
让我们近距离看一个经典的基于历史数据的构造图表例子 (图例. 1)。
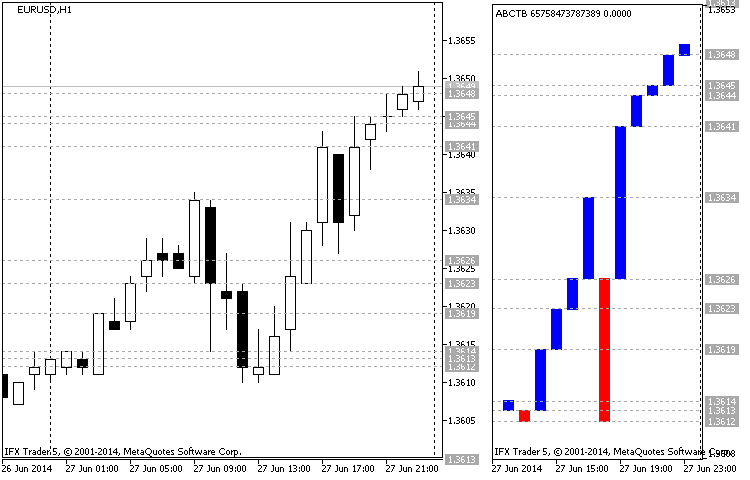
图例.1 构造一个三线突破图表示例 (EURUSD H1 27.06.2014)
图例. 1 在左侧呈现了一个蜡烛条图表,以及右侧的三线突破图表。这是 EURUSD 图表, 时间帧为 H1。图表的开始日期是 27.06.2014 起始价位 1.3613 (烛线的收盘时间 00:00), 则烛线 (01:00) 收盘于 1.3614, 形成了三线突破图表的第一根阳线。随后的空头烛线 (02:00) 形成一个阳线, 收盘于 1.3612 (收盘价低于之前的最低)。
后来多头烛条将价格推动到 1.3619 (03:00) 标记位置, 形成了一个新高,以及柱线。位于 04:00 的下跌烛线未能低于最低,并且它没有影响构造。位于 05:00 的烛线收盘于 1.3623, 标记了一个新高 (新的阳线)。
现在延续下降趋势, 我们需要经过两个最低 (1.3613), 但多头未放弃它们的位置,因此形成了一个新高 1.3626 (06:00)。后来多头试图扭转上行趋势两个小时, 但是相同的趋势持续,到达并创新高 1.3634 (09:00)。多头领先。现在绘制一根阳线, 经过三个最低价 (1.3626; 1.3623 和 1.3619)。
正如我们看到的, 在随后的三小时,空头在市场中占优, 下跌到位置 1.3612 (12:00)。它体现为一个新的阳线。但是,随后的五小时表明多头正在赢回自己的位置,并带领市场重回 1.3641,经过前高 1.3626,并在 17:00 形成新的阳线。空头在 18:00 未能超越前低,并且在随后五小时多头带领市场到达 1.3649,每小时形成一根新的阳线。
在我们得到代码之前,我们要说说指标本身,并找出是什么使它与众不同。三线突破很明显,就像其它指标,是专为高效率的市场分析,以及寻找新策略提供便利。我相信你一定想知道,此处是否有什么新奇。事实上,还真有一些。该指标可以改变计算的价格类型。它覆盖了所有四个标准价格条。构造图表的经典设计是仅针对一个类型,现代型则迎合所有四种价格类型 (开盘, 最高, 最低和收盘)。它修改了经典图表构造的外观,通过添加 "阴影" 使得它们看起来像日本蜡烛条,即加入了图表的视觉观感。
现代版本的特性还可以设置当数据缺失时优先同步价格数据。
图表构造的现代类型如图例 2 所示:
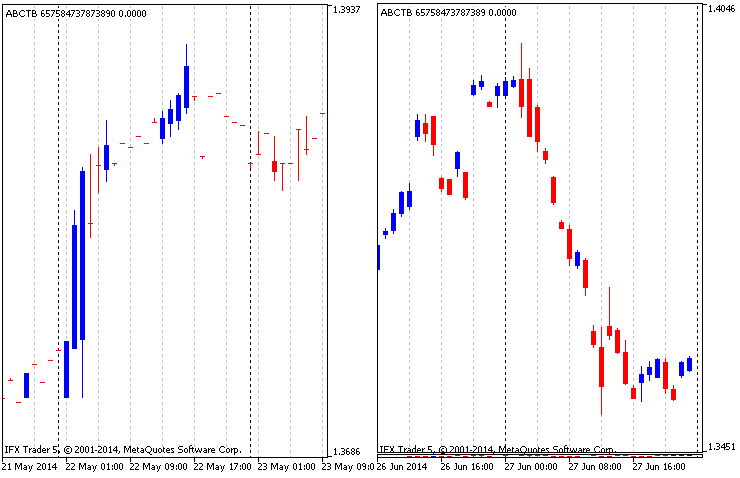
图例.2 修改后的基于四种价格类型图表
由于现代构造结合了四种不同价格类型的三线突破图表,它可以很自然地找到价格之间的差异。为了避免它,及时同步数据是必需的。价格同步带来两个变化: 完整 (图例. 2 右侧) 和局部 (图例. 2 左侧)。完整同步代表一个过滤的局部, 其中所有数据绘制在图表上,而且缺失数据被设置中的指定优选价格替代。在完整同步模式中,缺失数据被简单地省略,并且仅绘制数据完整的烛条。
另一项创新是周期分离,可便利的切分信号。正如您所知,周期分隔符可以在图表设置中启用。在指标中可以根据指定设置改变时间帧。不像 MetaTrader 5 中的图表, 通过垂直虚线分隔周期, 在此指标中通过一条变色垂直线表示(蜡烛, 图例. 3):
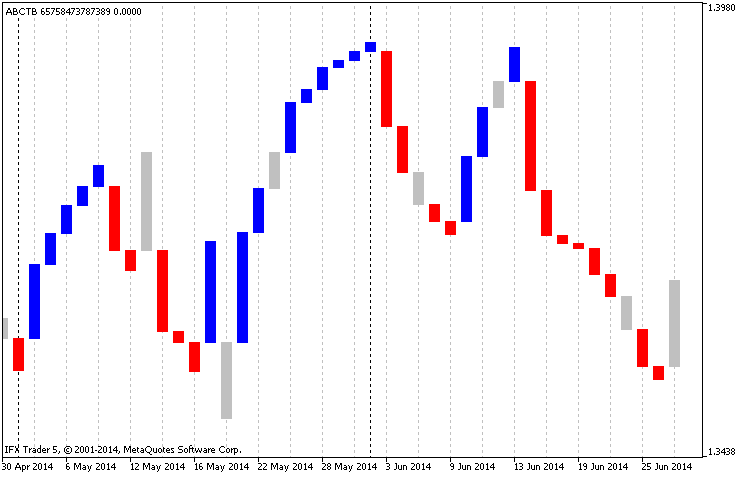
图例.3 指标中的周期分隔符
另外附加实现了技术指标 iMA, 其依据主图表的价格建立, 但是它可以及时与指标数据同步。因此,数据由均线过滤 (图例. 4):
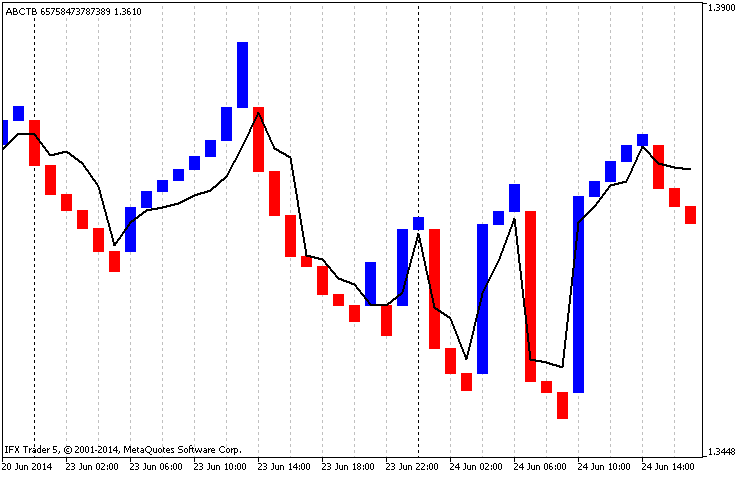
图例.4 内部均线
该指标还有一个特点,可以设置绘图的最小移动点数,以及所需反转的线数。它也是滤波器的作用。
指标的算法相当简单,它有三个阶段:复制数据,基于该复制数据进行计算,以及填充指标缓冲器(构造图表基于所接收的数据)。代码依据它们的内部以及输入数据联系被划分功能。让我们近距离观查这些代码。
1. 指标输入参数
该指标的序言中包含了图形结构的声明。在指标中它们有两个: 图表 "ABCTB" (DRAW_COLOR_CANDLES) 和附加均线 "LINE_TLB" (DRAW_LINE)。因此,有六个缓冲器。以下 enum(枚举) 类型用于提高界面设置以及设置本身:
然后我们声明缓存区数组, 用于计算的变量和结构。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ABCTB.mq5 | //| "Azotskiy Aktiniy ICQ:695710750" | //| "" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // ABCTB - Auto Build Chart Three Line Break #property copyright "Azotskiy Aktiniy ICQ:695710750" #property link "" #property version "1.00" #property indicator_separate_window #property indicator_buffers 6 #property indicator_plots 2 //--- plot ABCTB #property indicator_label1 "ABCTB" #property indicator_type1 DRAW_COLOR_CANDLES #property indicator_color1 clrBlue,clrRed,clrGreenYellow #property indicator_style1 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width1 1 //--- plot LINE_TLB #property indicator_label2 "LINE_TLB" #property indicator_type2 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color2 clrRed #property indicator_style2 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width2 1 //--- Price type for calculation enum type_price { close=0, // Close open=1, // Open high=2, // Hight low=3, // Low }; //--- type of chart construction enum type_build { classic=0, // Classic modified=1, // Modified }; //--- priority enum priority { highest_t=4, // Highest high_t=3, // High medium_t=2, // Medium low_t=1, // Low }; //--- input parameters input long magic_numb=65758473787389; // Magic number input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES time_frame=PERIOD_CURRENT; // Calculation time range input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES time_redraw=PERIOD_M1; // Period of chart updates input datetime first_date_start=D'2013.03.13 00:00:00'; // Start date input type_price chart_price=close; // Price type for calculation (0-Close, 1-Open, 2-High, 3-Low) input int step_min_f=4; // Minimum step for a new column (>0) input int line_to_back_f=3; // Number of lines to display a reversal(>0) input type_build chart_type=classic; // Type of chart construction (0-classic, 1-modified) input bool chart_color_period=true; // Changing color for a new period input bool chart_synchronization=true; // Constructing a chart only upon complete synchronization input priority chart_priority_close=highest_t; // Priority of the closing price input priority chart_priority_open=highest_t; // Priority of the opening price input priority chart_priority_high=highest_t; // Priority of the maximum price input priority chart_priority_low=highest_t; // Priority of the minimum price input bool ma_draw=true; // Draw the average input ENUM_APPLIED_PRICE ma_price=PRICE_CLOSE; // Price type for constructing the average input ENUM_MA_METHOD ma_method=MODE_EMA; // Construction type input int ma_period=14; // Averaging period //--- indicator buffers //--- buffer of the chart double ABCTBBuffer1[]; double ABCTBBuffer2[]; double ABCTBBuffer3[]; double ABCTBBuffer4[]; double ABCTBColors[]; //--- buffer of the average double LINE_TLBBuffer[]; //--- variables MqlRates rates_array[];// bar data array for analysis datetime date_stop; // current date datetime date_start; // start date variable for calculation //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Line Price | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct line_price// structure for storing information about the past lines { double up; // value of the high price double down;// value of the low price }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Line Information | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct line_info// structure for storing information about the shared lines { double up; double down; char type; datetime time; }; line_info line_main_open[]; // data on the opening prices chart line_info line_main_high[]; // data on the maximum prices chart line_info line_main_low[]; // data on the minimum prices chart line_info line_main_close[]; // data on the closing prices chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Buffer Info | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct buffer_info// structure for storing data for filling a buffer { double open; double high; double low; double close; char type; datetime time; }; buffer_info data_for_buffer[];// data for filling the modified construction buffer datetime array_datetime[]; // array for storing information of the time for every line int time_array[3]; // array for the function func_date_color datetime time_variable; // variable for the function func_date_color bool latch=false; // variable-latch for the function func_date_color int handle; // handle of the indicator iMA int step_min; // variable of the minimum step int line_to_back; // variable of the number of lines to display a reversal
2. 函数 OnInit
所有 指标缓存区 声明在函数 OnInit 中,以及指标数组设置如同 时间序列。
然后我们设置不会在图表上反映出来的指标数值, 设置 名称, 指定精度以及 删除当前数值,因为它们会造成图表过载。此处,我们还设置了指标 iMA 句柄,并检查输入数据的正确性。在出错的情况下,则输出相应的消息,并将数值改为最小。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- indicator buffers mapping //--- buffers for a chart SetIndexBuffer(0,ABCTBBuffer1,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer1,true); SetIndexBuffer(1,ABCTBBuffer2,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer2,true); SetIndexBuffer(2,ABCTBBuffer3,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer3,true); SetIndexBuffer(3,ABCTBBuffer4,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer4,true); SetIndexBuffer(4,ABCTBColors,INDICATOR_COLOR_INDEX); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBColors,true); //--- buffer for constructing the average SetIndexBuffer(5,LINE_TLBBuffer,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(LINE_TLBBuffer,true); //--- set the values that are not going to be reflected on the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(0,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0); // for the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(1,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0); // for the average //--- set the indicator appearance IndicatorSetString(INDICATOR_SHORTNAME,"ABCTB "+IntegerToString(magic_numb)); // name of the indicator //--- accuracy of display IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS,_Digits); //--- prohibit displaying the results of the indicator current value PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_SHOW_DATA,false); PlotIndexSetInteger(1,PLOT_SHOW_DATA,false); //--- handle=iMA(_Symbol,time_frame,ma_period,0,ma_method,ma_price); if(step_min_f<1) { step_min=1; Alert("Minimum step for a new column must be greater than zero"); } else step_min=step_min_f; //--- if(line_to_back_f<1) { line_to_back=1; Alert("The number of lines to display a reversal must be greater than zero"); } else line_to_back=line_to_back_f; //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
3. 复制数据函数
由于指标设计为与所有四种价格类型工作,则复制所有数据至关重要,包括时间。在 MQL5 中有一个结构名为 MqlRates。它用于存储有关交易时段的开始时间,价格,交易量和点差信息。
该函数的输入参数是起始和结束日期,时间帧及 MqlRates 类型的目标数组。如果复制成功此函数返回 true。数据将复制到中间数组。已计算缺失数据加上一个时段将复制至此,数据将被永久更新。如果复制到中间数组成功,则数据将被复制到数组中,以保证该函数地正确工作。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func All Copy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_all_copy(MqlRates &result_array[],// response array ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period, // timeframe datetime data_start, // start date datetime data_stop) // end date { //--- declaration of auxiliary variables bool x=false; // variable for the function response int result_copy=-1; // copied data count //--- adding variables and arrays for calculation static MqlRates interim_array[]; // temporary dynamic array for storing copied data static int bars_to_copy; // number of bars for copying static int bars_copied; // number of copied bars since the start date //--- find out the current number of bars in the time range bars_to_copy=Bars(_Symbol,period,data_start,data_stop); //--- count the number of bars to be copied bars_to_copy-=bars_copied; //--- if it is not the first time when data is being copied if(bars_copied>0) { bars_copied--; bars_to_copy++; } //--- change the size of the receiving array ArrayResize(interim_array,bars_to_copy); //--- copy data to a temporary array result_copy=CopyRates(_Symbol,period,0,bars_to_copy,interim_array); //--- check the result of copying data if(result_copy!=-1) // if copying to the temporary array was successful { ArrayCopy(result_array,interim_array,bars_copied,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); // copy the data from the temporary array to the main one x=true; // assign the positive response to the function bars_copied+=result_copy; // increase the value of the copied data } //--- return(x); }
4. 计算数据函数
此函数是数据计算的原型,用于构造经典的三线突破图表。正如已经提到的,该函数只计算数据,并将其插入代码开始处声明的结构类型 line_info 的指定数组。
此函数包含了另外两个函数: func_regrouping (重组函数) 和 func_insert (插入函数)。我们开始看看它们:
4.1. 重组函数
此函数重组相同方向的连续线的信息。它受限于传递到它的数组的尺寸,或是来自指标设置参数 line_to_back_f (显示反转的线数) 的精确值。所以,每次当控制传递到函数时,全部有关标识线的接收数据向下移动一点,并且索引为 0 的线会被填充新数值。
这就是突破所需线的信息如何被存储 (在经典构造为三线情况下)。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Regrouping | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_regrouping(line_price &input_array[],// array for regrouping double new_price, // new price value char type) // type of movement { int x=ArraySize(input_array);// find out the size of the array for regrouping for(x--; x>0; x--) // regrouping loop { input_array[x].up=input_array[x-1].up; input_array[x].down=input_array[x-1].down; } if(type==1) { input_array[0].up=new_price; input_array[0].down=input_array[1].up; } if(type==-1) { input_array[0].down=new_price; input_array[0].up=input_array[1].down; } }
4.2. 插入函数
该函数插入数值至响应数组。该代码很简单,不需要详细解释。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Insert | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_insert(line_info &line_m[], // target array line_price &line_i[], // source array int index, // array element being inserted char type, // type of the target column datetime time) // date { line_m[index].up=line_i[0].up; line_m[index].down=line_i[0].down; line_m[index].type=type; line_m[index].time=time; }
该用于计算数据的函数通常分为三个部分。第一部分,根据分析并依照操作符 switch 复制数据至中间数组。仅关注被复制价格。第二部分运行一个测试来计算数据数组所需的空间。然后该数据数组 line_main_array[], 初始化后传递到函数用于响应, 经历了一个变化。第三部分,轮流填充调整数据数组。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Build Three Line Break | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_build_three_line_break(MqlRates &input_array[], // array for analysis char price_type, // type of the price under analysis (0-Close, 1-Open, 2-High, 3-Low) int min_step, // minimum step for drawing a line int line_back, // number of lines for a reversal line_info &line_main_array[]) // array for return (response) of the function { //--- calculate the size of the array for analysis int array_size=ArraySize(input_array); //--- extract data required for calculation to an intermediate array double interim_array[];// intermediate array ArrayResize(interim_array,array_size);// adjust the intermediate array to the size of the data switch(price_type) { case 0: // Close { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].close; } } break; case 1: // Open { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].open; } } break; case 2: // High { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].high; } } break; case 3: // Low { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].low; } } break; } //--- enter the variables for storing information about current situation line_price passed_line[];// array for storing information about the latest prices of the lines (type structure line_price) ArrayResize(passed_line,line_back+1); int line_calc=0;// number of lines int line_up=0;// number of the last ascending lines int line_down=0;// number of the last descending lines double limit_up=0;// upper limit necessary to pass double limit_down=0;// lower limit necessary to pass /* Fill variables informing of the current situation with the first values */ passed_line[0].up=interim_array[0]; passed_line[0].down=interim_array[0]; //--- start the first loop to calculate received data for filling a buffer for drawing for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { if(line_calc==0)// no lines have been drawn { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } if(line_up>line_down)// last ascending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_up,line_back-1)].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<limit_down)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up=0; line_down++; } } if(line_down>line_up)// last descending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_down,line_back-1)].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>limit_up)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down=0; line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } } ArrayResize(line_main_array,line_calc);// change the size of the target array //--- zeroise variables and fill with the the initial data line_calc=0; line_up=0; line_down=0; passed_line[0].up=interim_array[0]; passed_line[0].down=interim_array[0]; //--- start the second loop to fill a buffer for drawing for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { if(line_calc==0)// no lines have been drawn { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } if(line_up>line_down)// last ascending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_up,line_back-1)].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<limit_down)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up=0; line_down++; } } if(line_down>line_up)// last descending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_down,line_back-1)].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>limit_up)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down=0; line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } } }
5. 图表构造函数
此函数的目的是依据选择的构造参数 (经典或修改) 计算图表数据并将显示数据填充到指标缓存区。如同之前函数, 此图表构造函数也有三个附加函数。它们是彩色函数, 同步函数以及均线函数。让我们来讨论更多它们的细节。
5.1. 彩色函数
此函数仅有一个输入参数 - 时间。该函数的响应是一个布尔变量。如果传递的数据是周期的边界,则该函数将返回 true。由于周期依赖于选择的时间帧,函数通过条件操作符 if 有一个内置的周期分隔。在周期被选择之后,它会检查是否一个新的周期已经开始。它是通过将日期转化为 MqlDateTime 结构并进行比较来完成。对于时间帧大于等于 H2, 日期值的变化指示新的周期开始。自时间帧 H12 至 D1,包含月份的变化,而在 W1 和 MN 之间,我们检查年份的变化。
不幸地, 结构 MqlDateTime 未包含当前周的信息。这个问题可以通过创建由变量 time_variable 表示的初始点来解决。依线向前,从这个日期中扣除一周的秒数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Date Color | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_date_color(datetime date_time) // input date { bool x=false;// response variable int seconds=PeriodSeconds(time_frame);// find out the calculation time range MqlDateTime date; TimeToStruct(date_time,date);// convert data if(latch==false) // check the state of the latch { MqlDateTime date_0; date_0=date; date_0.hour=0; date_0.min=0; date_0.sec=0; int difference=date_0.day_of_week-1; datetime date_d=StructToTime(date_0); date_d=date_d-86400*difference; time_variable=date_d; latch=true;// lock the latch } if(seconds<=7200)// period is less than or equal to H2 { if(time_array[0]!=date.day) { x=true; time_array[0]=date.day; } } if(seconds>7200 && seconds<=43200)// period is greater than H2 but less than or equal to H12 { if(time_variable>=date_time) { x=true; time_variable=time_variable-604800; } } if(seconds>43200 && seconds<=86400)// period is greater than H12 but less than or equal to D1 { if(time_array[1]!=date.mon) { x=true; time_array[1]=date.mon; } } if(seconds>86400)// period W1 or MN { if(time_array[2]!=date.year) { x=true; time_array[2]=date.year; } } return(x); }
5.2. 同步函数
同步函数有六个输入参数: 它们中的四个是优先价格, 布尔参数是完整或局部同步,以及它自己的分析数组。该函数被分成两部分: 完整与局部同步情况。
完整同步进行的三个阶段:
局部同步更加复杂。
传递一维数组结构数组并转化为二维, 其中第一个索引表示顺序,而第二个则是价格类型。之后介绍的是一个有四个元素的一维数组。价格优先级复制到该数组,然后数组进行排序,以确定优先顺序。之后,我们根据优先权使用循环 for 以及条件操作符 if 进行分派。与此同时, 如果优先权相同, 则价格序列如下: 收盘, 开盘, 最高, 最低。一旦操作符 if 发现第一个优先数值, 则循环 for 取代之前创建的二维数组中的所有 0 值等等。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Synchronization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_synchronization(buffer_info &info[], bool synchronization, char close, char open, char high, char low) { if(synchronization==true)// carry out a complete synchronization { int calc=0;// count variable for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(info); x++)// count complete data { if(info[x].close!=0 && info[x].high!=0 && info[x].low!=0 && info[x].open!=0)calc++; } buffer_info i_info[]; // enter a temporary array for copying ArrayResize(i_info,calc);// change the size of the temporary array calc=0; for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(info); x++)// copy data into the temporary array { if(info[x].close!=0 && info[x].high!=0 && info[x].low!=0 && info[x].open!=0) { i_info[calc]=info[x]; calc++; } } ZeroMemory(info); // clear the target array ArrayResize(info,calc); // change the size of the main array for(int x=0; x<calc; x++)// copy data from the temporary array to the main one { info[x]=i_info[x]; } } if(synchronization==false) // change zero values to priority ones { int size=ArraySize(info); // measure the size of the array double buffer[][4]; // create a temporary array for calculation ArrayResize(buffer,size); // change the size of the temporary array for(int x=0; x<size; x++) // copy data into the temporary array { buffer[x][0]=info[x].close; buffer[x][1]=info[x].open; buffer[x][2]=info[x].high; buffer[x][3]=info[x].low; } char p[4];// enter an array for sorting by the order p[0]=close; p[1]=open; p[2]=high; p[3]=low;// assign variables for further sorting ArraySort(p); // sort int z=0,v=0; // initialize frequently used variables for(int x=0; x<4; x++)// taking into account the results of the sorting, look through all variables and substitute them according to the priority { if(p[x]==close)// priority is for the closing prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=1; v<4; v++) { if(buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][0]; } } } if(p[x]==open)// priority is for the opening prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<4; v++) { if(v!=1 && buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][1]; } } } if(p[x]==high)// priority is for the maximum prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<4; v++) { if(v!=2 && buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][2]; } } } if(p[x]==low)// priority is for the minimum prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<3; v++) { if(buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][3]; } } } } for(int x=0; x<size; x++)// copy data from the temporary array back { info[x].close=buffer[x][0]; info[x].open=buffer[x][1]; info[x].high=buffer[x][2]; info[x].low=buffer[x][3]; } } }
5.3. 均线函数
它是最简单的函数。使用 OnInit 函数中接收到的指标句柄, 我们复制数值, 与传递到函数的参数日期相对应。之后这个数值作为响应返回到这个函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func MA | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double func_ma(datetime date) { double x[1]; CopyBuffer(handle,0,date,1,x); return(x[0]); }
该绘制图表的函数,通常分为两个部分:经典绘图与修改的。该函数有两个输入参数:价格类型用于构造 (在修改模式被忽略) 和构造类型 (经典和修改)。
在最开始,指标缓存区被清除,然后,依照构造类型分为两部分。第一部分(我们正在谈论的修改构造)开始调用该函数用来计算所有四个价格类型。然后,我们创建一个通用的数据数组,即我们复制所使用的数据,接收调用函数计算后的数据。之后,接收到的数据数组被排序,且复制数据被清除。在全局级别声明数组 array data_for_buffer[] 之后, 将会填充基于与下列数据同步的连续日期。填充指标缓存区是修改构造的最后阶段。
第二部分(经典构造)则简单很多。起初,数据计算的函数被调用,然后填满指标缓存区。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Chart Build | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_chart_build(char price, // price type for chart construction char type) // type of chart construction { //--- Zeroise the buffers ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer1); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer2); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer3); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer4); ZeroMemory(ABCTBColors); ZeroMemory(LINE_TLBBuffer); if(type==1)// construct a modified chart (based on all price types) { func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,0,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_close);// data on closing prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,1,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_open);// data on opening prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,2,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_high);// data on maximum prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,3,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_low);// data on minimum prices //--- calculate data arrays int line_main_calc[4]; line_main_calc[0]=ArraySize(line_main_close); line_main_calc[1]=ArraySize(line_main_open); line_main_calc[2]=ArraySize(line_main_high); line_main_calc[3]=ArraySize(line_main_low); //--- gather the date array int all_elements=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2]+line_main_calc[3];// find out the number of all elements datetime datetime_array[];// enter the array for copying ArrayResize(datetime_array,all_elements); int y[4]; ZeroMemory(y); for(int x=0;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// copy data into the array { if(x<line_main_calc[0]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_close[y[0]].time; y[0]++; } if(x<line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1] && x>=line_main_calc[0]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_open[y[1]].time; y[1]++; } if(x<line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2] && x>=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_high[y[2]].time; y[2]++; } if(x>=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_low[y[3]].time; y[3]++; } } ArraySort(datetime_array);// sort the array //--- delete replicated data from the array int good_info=1; for(int x=1;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// count useful information { if(datetime_array[x-1]!=datetime_array[x])good_info++; } ArrayResize(array_datetime,good_info); array_datetime[0]=datetime_array[0];// copy the first element as it is the pattern in the beginning of comparison good_info=1; for(int x=1;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// fill the new array with useful data { if(datetime_array[x-1]!=datetime_array[x]) { array_datetime[good_info]=datetime_array[x]; good_info++; } } //--- fill the buffer for drawing (colored candles) int end_of_calc[4];// variables of storing information about the last comparison ZeroMemory(end_of_calc); ZeroMemory(data_for_buffer); ArrayResize(data_for_buffer,ArraySize(array_datetime));// change the size of the declared global array for storing data before passing it to a buffer for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(array_datetime); x++) { data_for_buffer[x].time=array_datetime[x]; for(int s=end_of_calc[0]; s<line_main_calc[0]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_close[s].time) { end_of_calc[0]=s; if(line_main_close[s].type==1)data_for_buffer[x].close=line_main_close[s].up; else data_for_buffer[x].close=line_main_close[s].down; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[1]; s<line_main_calc[1]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_open[s].time) { end_of_calc[1]=s; if(line_main_open[s].type==1)data_for_buffer[x].open=line_main_open[s].down; else data_for_buffer[x].open=line_main_open[s].up; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[2]; s<line_main_calc[2]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_high[s].time) { end_of_calc[2]=s; data_for_buffer[x].high=line_main_high[s].up; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[3]; s<line_main_calc[3]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_low[s].time) { end_of_calc[3]=s; data_for_buffer[x].low=line_main_low[s].down; break; } } } //--- start the function of synchronizing data func_synchronization(data_for_buffer,chart_synchronization,chart_priority_close,chart_priority_open,chart_priority_high,chart_priority_low); //--- preparatory actions before starting the function func_date_color ZeroMemory(time_array); time_variable=0; latch=false; //--- fill the buffer for drawing candles for(int x=ArraySize(data_for_buffer)-1,z=0; x>=0; x--) { ABCTBBuffer1[z]=data_for_buffer[x].open; ABCTBBuffer2[z]=data_for_buffer[x].high; ABCTBBuffer3[z]=data_for_buffer[x].low; ABCTBBuffer4[z]=data_for_buffer[x].close; if(ABCTBBuffer1[z]<=ABCTBBuffer4[z])ABCTBColors[z]=0; if(ABCTBBuffer1[z]>=ABCTBBuffer4[z])ABCTBColors[z]=1; if(func_date_color(data_for_buffer[x].time)==true && chart_color_period==true)ABCTBColors[z]=2; if(ma_draw==true)LINE_TLBBuffer[z]=func_ma(data_for_buffer[x].time); z++; } } else// construct a classic chart (based on one price type) { func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,price,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_close);// find data on selected prices ArrayResize(array_datetime,ArraySize(line_main_close)); //--- preparatory actions before starting the function func_date_color ZeroMemory(time_array); time_variable=0; latch=false; //--- the buffer for drawing candles for(int x=ArraySize(line_main_close)-1,z=0; x>=0; x--) { ABCTBBuffer1[z]=line_main_close[x].up; ABCTBBuffer2[z]=line_main_close[x].up; ABCTBBuffer3[z]=line_main_close[x].down; ABCTBBuffer4[z]=line_main_close[x].down; if(line_main_close[x].type==1)ABCTBColors[z]=0; else ABCTBColors[z]=1; if(func_date_color(line_main_close[x].time)==true && chart_color_period==true)ABCTBColors[z]=2; if(ma_draw==true)LINE_TLBBuffer[z]=func_ma(line_main_close[x].time); z++; } } }
6. 整合函数
此功能联合所有控制指标元素。首先,当前日期被定义,之后复制数据函数和图表构造函数被调用。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Consolidation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_consolidation() { //--- defining the current date date_stop=TimeCurrent(); //--- copying data for analysis func_all_copy(rates_array,time_frame,first_date_start,date_stop); //--- basic construction of the chart func_chart_build(chart_price,chart_type); ChartRedraw(); }
7. 键盘控制和自动控构造制函数
这些函数被设计为通过按键盘上的 "R" 键 (OnChartEvent) 或按照选定的时间范围 (OnCalculate) 自动重绘指标。后者则通过新柱线函数 (func_new_bar) 进行分析,func_new_bar 是一个曾描述过的 IsNewBar 函数简化版。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const int begin, const double &price[]) { //--- if(func_new_bar(time_redraw)==true) { func_consolidation(); }; //--- return value of prev_calculated for next call return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ChartEvent function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnChartEvent(const int id, const long &lparam, const double &dparam, const string &sparam) { //--- event of a keystroke if(id==CHARTEVENT_KEYDOWN) { if(lparam==82) //--- the key "R" has been pressed { func_consolidation(); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func New Bar | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_new_bar(ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period_time) { //--- static datetime old_times; // variable of storing old values bool res=false; // variable of the analysis result datetime new_time[1]; // time of a new bar //--- int copied=CopyTime(_Symbol,period_time,0,1,new_time); // copy the time of the last bar to the cell new_time //--- if(copied>0) // everything is ок. data copied { if(old_times!=new_time[0]) // if the old time of the bar is not equal to the new one { if(old_times!=0) res=true; // if it is not the first start, then new bar = true old_times=new_time[0]; // remember the time of the bar } } //--- return(res); }
在这一点上,我们必须完成描述指标的代码,并谈谈使用它的方式。
让我们开始基于经典图表构造来分析主要策略。
1. 白与黑线作为买卖信号
大致我们可以谈论两个规则:
让我们看看图例. 6,显示的是EURUSD 从2013年开始的经典构造(所分析的时间范围如图例. 5 描绘)。
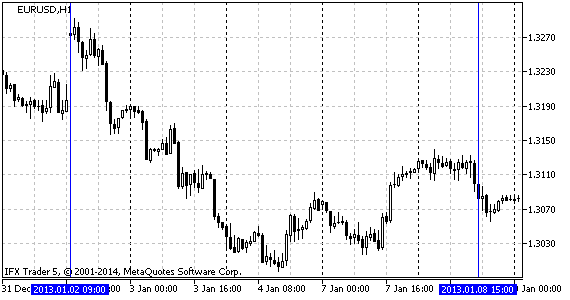
图例.5 分析时间范围 EURUSD H1
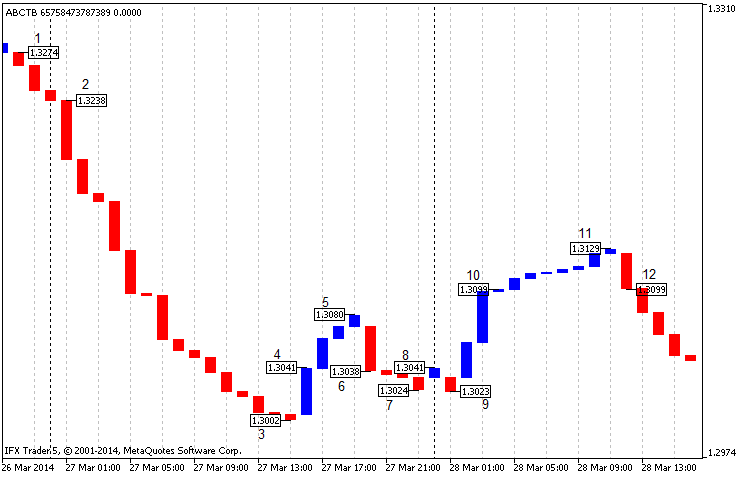
图例.6 三线突破图表经典构造 EURUSD H1, 开始自 2013, 收盘价格
在图表上 (图例. 6) 我们可以清晰看到在点 1 和 2 之间的信号 (规则一) , 即起始卖点。在这种情况下,按照四位数字报价,收入超过 200 点。随后的点 4 说明有利买入 (规则二)。截至收盘,在点 5 的利润为 40 点,而我们的盈亏平衡点处于收盘价点 6。
在点 6 我们可以看到卖信号 (规则二)。在收盘价点 7,我们获得 10 点利润,在收盘价点 8 则盈亏平衡。点 8 和 9 不可以考虑作为信号,因为它们既不满足规则一,也不满足规则二。我们可以在点 10 (规则一) 买入; 我们也可以在收盘价点 11 获得 20 点利润,或在点 12 盈亏平衡。所有数字均四舍五入。
在最好的情况下,使用这种策略,我们可以产生 270 点的利润,这很令人印象深刻。同时,在指定的时间范围内有强烈的走势从而影响利润。在最坏的情况下,交易可能会导致盈亏平衡,这其实还不坏。
值得一提的是,当情况既符合规则一也符合规则二,我们需要在相同趋势中,等待一个代表趋势反转的行确认。
2. 等距通道,支撑与阻力线
另一种交易策略是运用三线突破图表进行技术分析。让我们看看图例. 7:
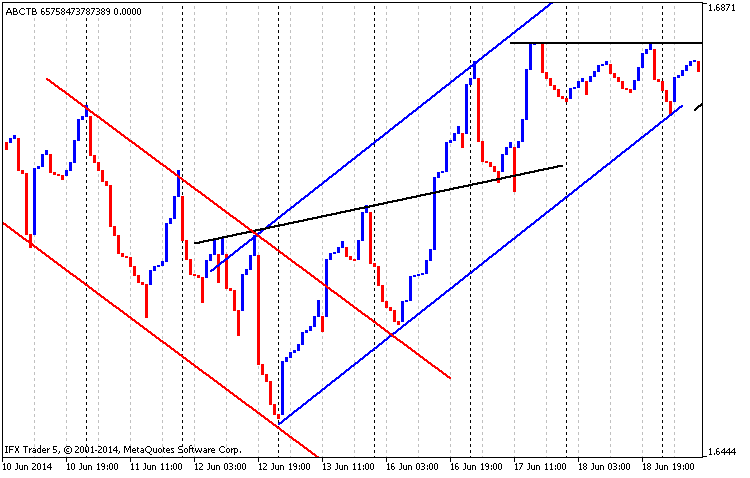
图例. 7 等距通道, 支撑与阻力线, GBPUSD H1, 时间范围自 01.03.2014 至 01.05.2014
在图例. 7 中您可以看到下降等距通道以红色线绘制,上升等距通道为蓝色,而支撑与阻力线以黑色绘制。很显然,所述第一阻力线正切入支撑线。
3. 蜡烛条形态
一个修改过的图表 (两线突破) 时间帧为 M30,货币对为 USDCAD,开始自 2013,看上去很有趣。
我们可以区分日本蜡烛条形态作为合理的信号 (图例. 8)。

图例. 8 修改的三线突破图表, USDCAD M30, 开始自 2013, 两线突破
在图表开始,我们可以看到反转形态 "Engulfing(吞噬)" 位于标记 1 之下。它由两根烛台组成: 红色和前面的蓝色。上升趋势线之后,市场走低到 2 号位置,是一个烛台反转形态 "Hammer (锤)"。在这个点上,市场改变方向。同样的情况出现在形态 3 处("Spinning Top -- 陀螺")。随后反转形态 "Kharami (孕育线)" (位置 4 ) 显示为烛条 4 以及它旁边的长阳线。形态 6 也由两根烛条组成 (形态 "Engulfing--吞噬") 但不像第一根类似模型,它令市场反方向翻转。
因此,可以得出结论,使用该指标分析是可以接受的,但它有这样的缺点,如信号较少,以及可能有显著的回撤。这一策略当然需要进一步发展。
4. 移动均线
局部修改,如添加移动均线,仅绘制线条,可为分析给与新的机会。
让我们看看图例. 9:
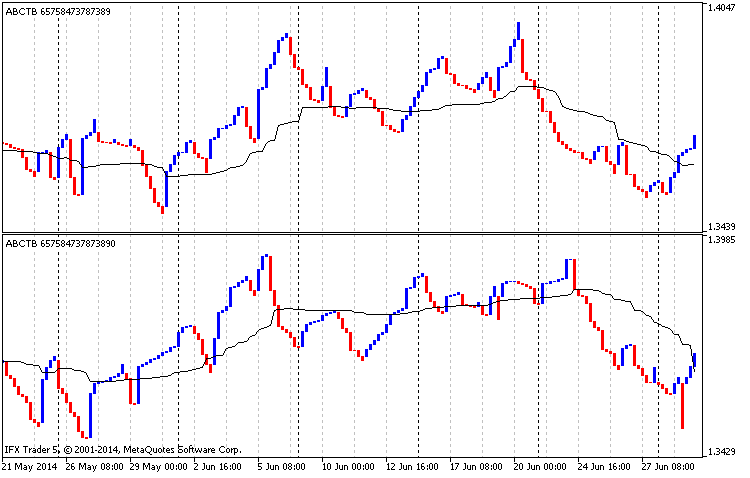
图例.9 分析移动均线, EURUSD H4, 三线突破图表, 经典构造, 自 01.01.2014 至 01.07.2014
在图例. 9 的上半部描绘了一幅给予最高价的经典构造图表,以及均线 (平均周期为 90, 最低价, 平滑平均)。图的下半部显示一个基于最低价的经典构造图表,以及均线 (平均周期为 90, 最高价, 平滑平均)。
所以,在图例. 9 的上半部分,均线可以被认为是支撑线,在下半部,与此相反,为阻力线。如果在两个图表中的价格均低于平均水平,则目前市场上呈下降趋势,此刻最好卖出。当价格上升到高于平均水平,此刻是时候买入。此策略的一个缺点是,它是只适用于长线交易。
最后,我可以说,三线中断图表始终给出良好的信号,或者在最坏的情况下,也会导致盈亏平衡。实践证明,最好在一个长线趋势中应用,因此,我不建议在短线交易使用这种图表。如果任何人有关于如何使用它进行交易的新思路,我很乐意讨论它。
通常情况下,我试着来详细揭示代码。再次,若有任何扩展,返工或优化的想法,请为本文书写评论。

本社区仅针对特定人员开放
查看需注册登录并通过风险意识测评
5秒后跳转登录页面...
移动端课程
